Describe the Mechanism by Which Supply Creates Its Own Demand
They use this additional income to demand goods of an equivalent value to those they supply. Supply creates its own demand.
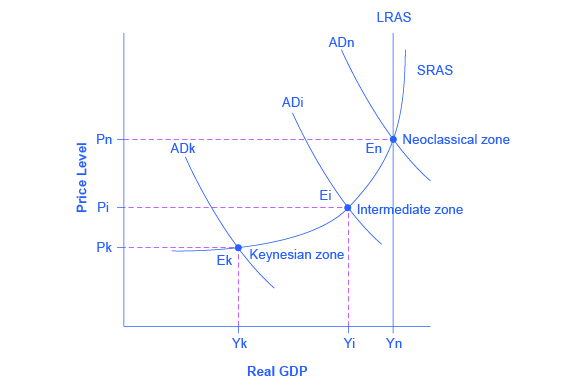
Keynes Law And Say S Law In The Ad As Model Article Khan Academy
Supply creates its own demand.

. Says Law and the Macroeconomics of Supply. In order to supply goods suppliers must employ workers whose incomes increase as a result of their labor. Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply.
When consumers demand more goods than are available on the market prices are driven higher and the additional opportunities for profit induce more suppliers to enter the market producing an equivalent amount to that which is demanded. In particular quite a few economists seemed utterly unaware that. The short run aggregate supply curve was constructed assuming that as the price of outputs increases the price of inputs stays the same.
Describe the mechanism by which supply creates its own demand. The short run aggregate supply curve was constructed assuming that as the price of outputs increases the price of inputs stays the same. The forces of supply and demand in individual markets will cause prices to rise and fall.
Says law states that the production of goods creates its own demand. Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply. Briefly stated it means that supply creates its own demand.
It is worthwhile to remark that a product is no sooner created than it from that instant affords a market for other products to the full extent of its own value J. Supply creates its own demand is the formulation of Says law. Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply.
According to Says law aggregate production necessarily creates an equal amount of aggregate demand. Says law also known as Says law of markets in Classical economics states that supply itself creates its own demand. In 1803 John Baptiste Say explained his theory.
Neoclassical economists emphasize Says law which holds that supply creates its own demand. Keynesian economists emphasize Keynes law which holds that demand creates its own supply. What is potential GDP.
So somebody is the supplier the supplier is supplying whatever goods there are to purchase and then some buyer is purchasing. Eight Powerful Ideas 3 Scarcity Trade-offs And Production Possibilities 4 Demand Supply And Market Equilibrium 5 Markets In Motion And Price Controls 6 Elasticities 7 Market Efficiency And Welfare 8. The bottom line remains however that every sale represents income to someone and so Says Law argues a given value of supply must create an equivalent value of demand somewhere else in the economy.
3The short run aggregate supply curve was constructed assuming that as the price of outputs increases the price of inputs stays the same. So each addition to supply is accompanied by an intended addition to demand. The short run aggregate supply curve was constructed assuming that as the price of outputs increases the price of inputs stays the same.
In other words every producer who brings goods lo the market does so only to exchange them for other goods. 2Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply. Keynesian economists emphasize Keynes law which holds that demand creates its own supply.
Describe the mechanism by which supply creates its own demand. Name some factors that could cause AD to shift and say whether they would shift AD to the right or to the left. If your MPC -06 and government spending G increases by.
Neoclassical economists emphasize Says law which holds that supply creates its own demand. Because Jean-Baptiste Say Adam Smith and other. As a matter of historical accuracy it seems clear.
When consumers demand more goods than are available on the market prices are driven higher and the additional opportunities for profit induce more suppliers to enter the market producing an equivalent amount to that which is demanded. Many mainstream economists take a Keynesian perspective emphasizing the importance of aggregate demand for the short run and a neoclassical perspective emphasizing the. When consumers demand more goods than are available on the market prices are driven higher and the additional opportunities for profit induce more suppliers to enter the market.
The rejection of this doctrine is a central component of The General Theory of Employment Interest and Money 1936 and a central tenet of Keynesian economics. November 3 2015 123 pm. Demand Creates Its Own Supply.
How would an increase in the prices of important inputs like energy. He asserted that there cannot be any general over-production or general unemployment in the economy as whatever is produced is automatically consumed. Spending multiplier 11-MPC 5.
Moreover the act of production creates an additional item of value for which other things can be exchanged. One of the intellectually horrifying things about the response to economic crisis was the way many economists some of them famous reinvented old fallacies in the belief that they were saying something profound. Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply When consumers demand more goods than are available on the market prices are driven higher and the additional opportunities for profit induce more suppliers to enter the market producing an equivalent.
November 3 2015 123 pm. Describe the mechanism by which supply creates its own demand. The Effect of Government Spending.
Pp1389 This view suggests that. Describe the mechanism by which supply creates its own demand. It is an economic rule that production is the source of demand so says Says law.
1 The Role And Method Of Economics 2 Economics. See Principle of effective demand which is an affirmative form of the negation of Says law. This idea that supply creates his own demand comes from the economist jean Baptiste and what they say is that supply creates its own demand in the sense that for everything that we for everything that is supplied someone has to buy.
Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply. Describe the mechanism by which demand creates its own supply. Those economists who emphasize the role of supply in the macroeconomy often refer to the work of a famous French economist of the early nineteenth century named Jean-Baptiste Say 17671832.
Describe the mechanism by which supply creates its own demand. They use this additional income to demand goods of an equivalent value to those they supply.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/jean-baptiste-say_round3-4b8d65fd5fde497296e774cb6f8008c4.png)
Say S Law Of Markets Definition

Comments
Post a Comment